VR6 cylinder head overhaul
Valve springs
The maximum allowable clearances for engines 2.0 and 2.8 are the same.
Volkswagen T4 cylinder head , then the dimension "a" (see Fig. 152) must be at least 139.50 mm. The nominal size is 140 ± 0.1 mm. To replace the guide, use a drift to knock out the old valve guide from the camshaft side, as shown in Fig. 153. The new valve guide is pressed in on the same side. The cylinder head can be heated to facilitate repair.
Rice. 153 Removing the valve guide
If you have replaced the valve guides, you must replace the valves and lap the valves against the seats.
♦ Lubricate the new guides with engine oil and press them from the camshaft side into the cold cylinder head until the guide shoulder rests on the cylinder head.
Once pressed in, the valve guides should be reamed using the special reamer 3120. This reamer will automatically provide a diameter of 7.0mm plus tolerance (plus) for the valve stems.
If you do not have such a sweep, then you can use an adjustable sweep. Reverse 7.0mm diameter guides for both intake and exhaust valves. After machining the holes, the valve seats must be further machined. Valve Seats
If the camshaft bearings are worn out, it is best to replace the cylinder head assembly.
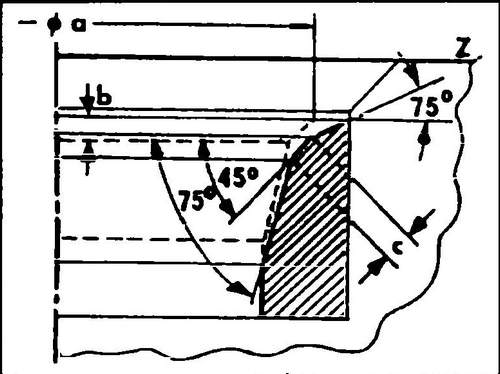
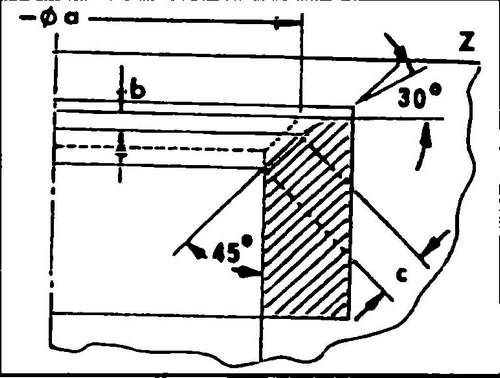
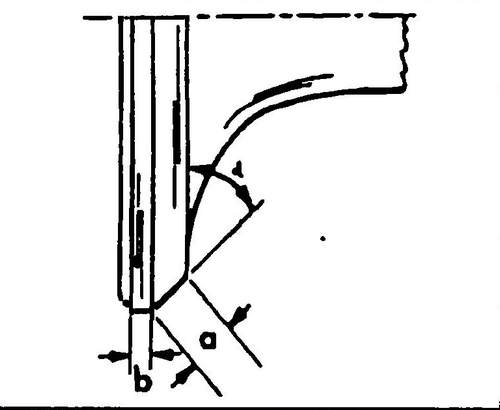
This eliminates the need for finishing procedures. In other cases, it is necessary to check and correct the working chamfers of the valve seats: ♦ Check the condition and degree of wear of the valve seats. Small traces of wear can be removed with a 45º cutter. If the valve seats are badly damaged, they must be reground. The angles to be obtained during milling are shown in fig. 154 and 155. It should be remembered that the diameter of the working chamfer of the inlet and exhaust valve seats are different.
Rice.
154 Inlet valve seat geometry: - valve seat diameter, in - maximum allowable machining allowance, c - width of the valve seat chamfer, Z - lower edge of the block head
Rice.
155 Exhaust valve seat geometry: a - valve seat diameter, b - maximum allowable machining allowance, c - valve seat width, Z - lower edge of the block head
The following measurements must be taken to determine the "b" dimension of the possible machining:
♦ Insert the valve into its guide and press firmly against the seat.
♦ Measure the distance between the valve cover seat and the valve face (see fig. 156).
Pic. 156 Valve Depth Measurement
♦ Calculate the maximum allowable machining allowance (based on the measurement result and the minimum allowable value).
For intake valves, this size is 33.9 mm, for exhaust valves - 34.1 mm. If we subtract the minimum allowable distance from the obtained measurement result, we will obtain the maximum allowable allowance "in" (see Fig. 154 and 155). This must be taken into account, proceed as follows: Valve seats must be milled after replacing the valve guides:
♦ First of all, a 45º angle must be made, and then with a 30º cutter lightly machine the upper edge of the seat to reduce the width of the chamfer to 1.7 mm for intake valves and in 2.0 mm for exhaust valves.
The depth of the valves during the processing of the seat increases.
When milling, it is necessary to ensure that the maximum allowable size of this recess is not violated. To avoid excessive penetration of the valve into the head of the block, it is necessary to carry out the measurements described above (otherwise the mode of operation of the valve springs changes). Valve seats, after milling, must be lapped.
Lapping of valves is described in detail in the section. Valves
Minor defects in the working chamfer of the valve plate during the repair of the Volkswagen T4 cylinder head can be eliminated during grinding.
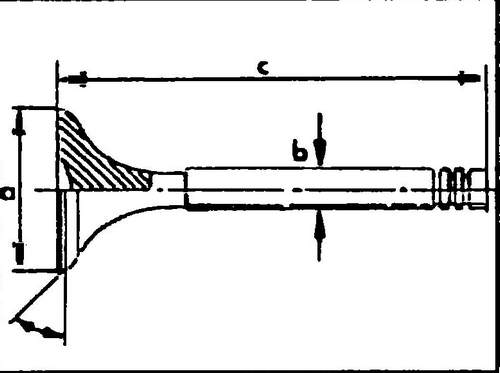
♦ Measure the valves according to fig. 157, replace any valves that are out of specification.
Rice.
157 Main dimensions of valves
If wear is found on the ends of the valve stems, then they can be cut on the machine, provided that the layer is removed no more than 0.50 mm.
Inlet valve plates can be ground using a special machine, provided that the “b” dimension (see Fig. 158) is not less than 0.5 mm. Machining of exhaust valves is not allowed, as they have a special design (with a sodium filler). Minor damage can be repaired by lapping. For disposal, such a valve must be taken to a VW service station. In no case should they simply be thrown away, as an extreme measure (not the safest) you need to saw through the stem and throw the valve into a barrel of water.
Rice. 158 Valve face geometry
Cylinder head
♦ Thoroughly clean the seating surfaces of the Volkswagen T4 head and cylinder block when repairing, check for warping of these surfaces.
The verification procedure is described in detail in the section. If warpage exceeds 0.10 mm, then the cylinder head should be ground on an appropriate machine. If more, then the block head should be replaced. Camshaft
The camshafts are each designed for the respective cylinder bank, as
have a similar but different design (distributor drive). By number you can determine for which bank of cylinders which shaft is intended: Shaft for cylinder bank 1.3 and 5.....021109101M
Shaft for cylinder bank 2.4 and 6......021109102A
It is necessary to carry out some checks, before reinstalling the removed camshaft in the engine.
♦ Check for runout on the middle journal as described in section.
If the runout exceeds 0.01 mm per full revolution, then the camshaft must be replaced, since the shafts cannot be straightened. ♦ Then visually inspect the condition of the bearing journals and the shaft for any visible defects.
Shafts that are damaged or show signs of wear must be replaced. ♦ Measure the end play of each shaft as described in the section. The gap should not exceed 0.15 mm. Otherwise, the thrust surfaces of the bearing cover are worn out.
Correct timing belt replacement Volkswagen T4 . Volkswagen T4 engine .